Summary
Museums Victoria holds significant collections of artworks by Australian Aboriginal artists dating from the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. This painting is amongst the earliest works collected by the director of the National Museum of Victoria, Walter Baldwin Spencer, who went to Oenpelli in 1912. Oenpelli was a pastoral lease taken up in 1906 by the legendary Northern Territory figure Paddy Cahill. Spencer returned to Melbourne with thirty-eight works on bark that had been removed from the wet season shelters in the area of the East and South Alligator Rivers. The collaboration between these two men over the following decade would result in the commissioning of over 170 bark paintings for the museum. The imagery in the works derive from a vast array of animals that are depicted in the rich rock art of the region, as well as a significant number of spirit figures known to bining, the people of western Arnhem Land. The bark paintings in the Spencer Collection and the Paddy Cahill Collection are considered the most significant historical art works from western Arnhem Land, and often feature in national and international exhibitions and publications. These paintings take pride of place amongst the extensive and significant holdings of Aboriginal art in the Indigenous collections at Museums Victoria. The only earlier known bark paintings are in the Macleay Museum in Sydney and date from 1878 and were collected at Port Essington.
Physical Description
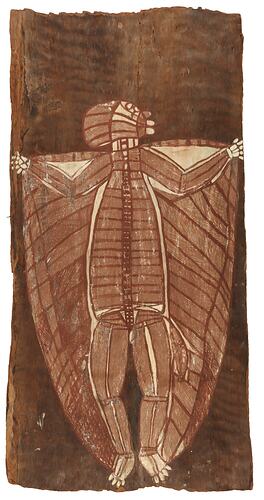
A single sheet of eucalyptus bark, stringybark (Eucalyptus tetrodonta), painted with natural pigments. The image of a single bat-like male figure.
Significance
This image is of a male spirit associated the country of the 'tribe' that Baldwin Spencer identified as 'Geimbo'. These are in fact Erre, Mengerridji and Urningank people and traditional owners for the area around Oenpelli. Spencer recorded 'Warraguk' as the name of this spirit who walks around in the day looking for 'sugarbag' (honey) and then rests at night by hanging like a bat from trees in 'bamboo country'. The depiction here is a front view of the figure. The prominent and distinctive head, face and hair conforms to the particular convention of representing the features of this spirit figure, although the head is unusually painted as a side profile. The bat-like wings here are the specific feature that allows for the spirit's identity to be established. This painting featured in 'Art of Australia', an exhibition at the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York in 1941, and was exhibited in Spencer Hall at the original site of the museum in Russell Street and is listed in the Guide to the Australian Ethnological Collection in National Museum of Victoria published in 1922.
More Information
-
Object/Medium
Painting, bark
-
Maker
-
Cultural Groups
-
Locality
Oenpelli, Western Arnhem Land, Northern Territory, Australia
-
Date Produced
-
Collector
-
Date Collected
-
Object Measurements
790 mm (Width), 30 mm (Depth), 1530 mm (Height)
65,000 Years: A short history of Australian Art. The University of Melbourne.
-
Keywords
-
References
[Book] Spencer, Walter B. 1922. Guide to the Australian Ethnological Collection : exhibited in the National Museum of Victoria. 142.
-
Collection Names
-
Type of item
-
Discipline
-
Category
-
Collecting Areas
Australian Indigenous - Northern Australia and Queensland and Torres Strait Islands
-
Medium
Natural pigments
-
Technique
Painting
-
Support
Eucalyptus bark