General Description
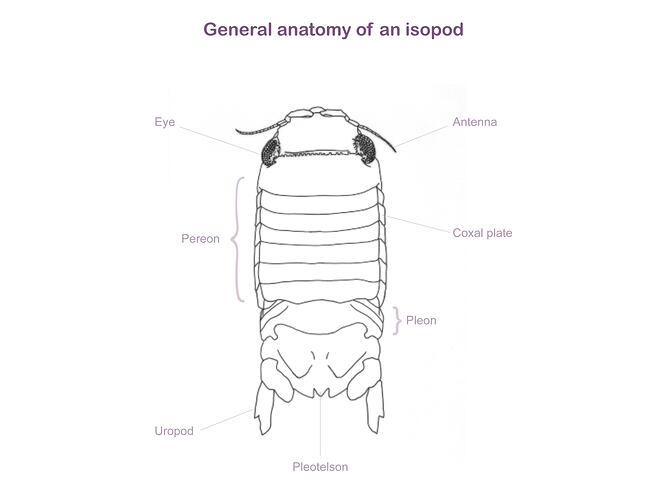
Body cylindrical, with prominent antennae. The first four pairs of legs are thin and with rows of hairs; the last three pairs are more stubby and attach the animal. Top of head with distinct "bump" between the eyes, body up to 11 mm long.
Biology
Neastacilla species, commonly known as skeleton louse, are often overlooked in their natural surroundings because they resemble the algae in which they live. All species of this genus use the long hairs on the front legs to filter planktonic food from the water.
Distribution
Southern temperate oceans, including south-eastern Australia.
Habitat
Subtidal to depths of 115 m.
More Information
-
Animal Type
-
Animal SubType
-
Brief Id
Body cylindrical, antennae prominent, with thin filtering legs in the front and short legs at the back. Fourth body segment extraordinarily long with body bent at a right angle to hold feeding legs up.
-
Maximum Size
11 mm
-
Habitats
-
Diet
Plankton or Particles
-
Diet Categories
Organic matter
-
Endemicity
-
Commercial
No
-
Conservation Statuses
DSE Advisory List: Not listed, EPBC Act 1999: Not listed, IUCN Red List: Not listed
-
Depths
Shallow (1-30 m), Deep ( > 30 m)
-
Water Column Locations
On or near seafloor
-
Taxon Name
-
Scientific Author
(Guiler, 1949)
-
Common Name
Skeleton Louse
-
Phylum
-
Subphylum
-
Superclass
-
Class
-
Subclass
-
Superorder
-
Order
-
Suborder
-
Family
-
Genus
-
Species Name
inaequispinosa