On 1 January 1842 the Port Phillip Savings Bank opened. It was the offspring of the Bank of New South Wales and the progenitor of the State Savings Bank of Victoria. An earlier Port Phillip Bank had opened in 1839, but was short-lived. The first Board of Trustees included Charles Joseph La Trobe as President, who had recommended the Bank's establishment.
By 1848 there were 641 depositors' accounts held in Melbourne, and by 1850 branches had opened in Geelong and Port Fairy.
In November 1852, when the separation of the colony of Victoria was being facilitated, a Savings Bank of Port Phillip Laws Amendment Bill was introduced. The bill proposed to continued the Port Phillip Bank as the 'Savings Bank of Victoria'. The Bank would operate as a single institution with separate branches. The bill was referred to a select committee for further consideration. The committee unwisely decided that each branch of the Savings Bank should operate as a separate institution, overseen by a Board of Commissioners - as was the case in Britain and New Zealand. It came to this decision under the influence of the inexperienced English barrister Dr George MacKay. On 7 February 1853 the Act to Consolidate and Amend the Laws Relating to Savings Banks was passed. It came into effect on 30 June 1853.
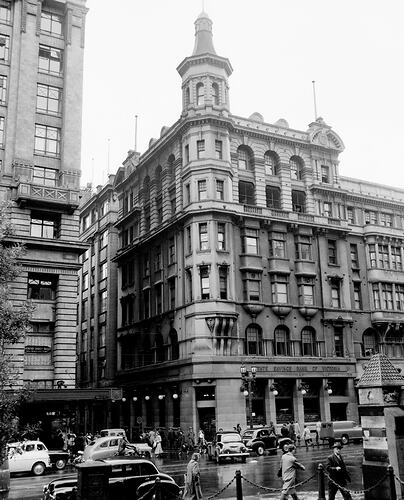
In 1858 a head office opened on the corner of Market Street and Flinders Lane. It remained in this location until 1912.
Between 1857 and 1865 several regional banks were opened under the auspices of the State Savings Bank of Victoria. By 1862 the Commissioners were trying to limit the number of banks opening. Customer numbers continued to grow, however, and by 1890 there were 177,189 bank accounts held in Victoria.
Various attempts were made to amalgamate the banks, and in 1894-95 a Royal Commission was finally held to consider amalgamation and improved bank assistance to farmers. It recommended amalgamation, and on 24 December 1896 the unifying Savings Bank Act 1481 came into effect.
On 1 October the following year the Post Office Savings Bank merged with the State Savings Bank.
In the 1920s the State Savings Bank created a housing estate in Port Melbourne, one of a number of actions to encourage home ownership in the early to mid 20th century. After World War II the Bank began lending on overdraft to the co-operative housing societies. By June 1954 some 51 societies had received overdraft facilities from the State Savings Bank, amounting to £15.7 million.
In 1970 the Bank issued a medal to commemorate the bicentenary of the arrival of Captain James Cook [NU 33158].
On 1 January 1991 the State Savings Bank of Victoria officially merged with the Commonwealth Bank.
References:
History of the Bank are available in Craddock, Trevor, (1967). 125 Years: The Story of the State Savings Bank of Victoria
Abbott, Malcolm J. (1997). A History of the Victorian Co-operative Housing Societies, 1944-1996, Working Paper Series No. 9702, January, Deakin University http://www.deakin.edu.au/fac_buslaw/sch_'ef/publications/wp/wp9702%20.pdf.
Photographs, housing design books, map and plan collection, General Manager's Department correspondence, Commissioners' minute books and annual reports from the State Bank of Victoria are held by the Public Record Office, Victoria.
More Information
-
Keywords
-
Localities
-
Authors
-
Article types