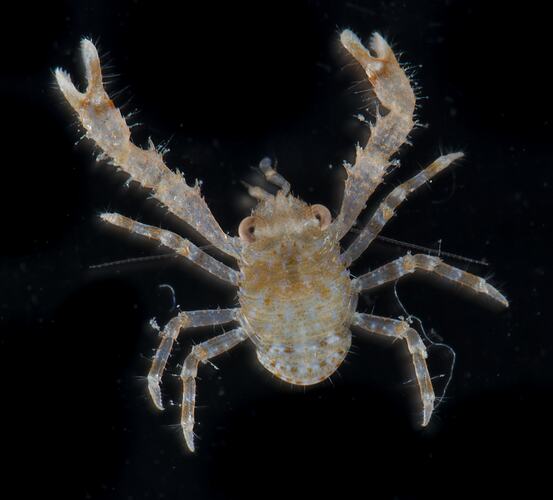
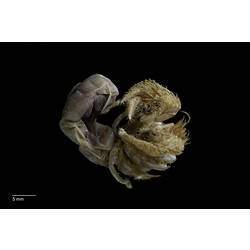
General Description
Though all decapods have ten legs, anomurans are characterised by the reduction in size of the last pair of legs. This gives them an eight-legged appearance that separates them from true crabs. The coconut crab is the largest anomuran, and in fact the largest arthropod in the world. The red king crab can also reach great sizes, with a leg span of up to 1.8 m
Biology
There are several different body forms among the anomurans, however carcinisation has occurred in several instances. Carcinisation is a theoretical evolutionary trend towards a crab-like body form. A study of anomuran molecular data showed that carcinisation has occurred independently at least three times since their first divergence around 250 million years ago. This is best seen in the porcelain crabs and king crabs. Where true crabs (Brachyura) have a tiny abdomen that sits folded under the body, anomurans may have a larger abdomen that is elongated or folded in on itself. This means that anomurans cannot move as fast as the true crabs. Squat lobsters more closely resemble true lobsters with long chelipeds (legs with claws). Most anomurans live in warmer temperate or tropical marine areas, but representatives are found all around the world. Some squat lobster species, including the bizarrely hairy-looking yeti crab Kiwa hirsuta have even been found on toxic hydrothermal vents. Though crustaceans are generally scavengers or opportunistic carnivores, feeding habits of anomurans varies greatly. Coconut crabs feed on fleshy fruits and nuts as well as smaller animals. Munidopsis andamanica is a herbivorous species of deep- sea squat lobster that feeds exclusively on decaying wood on the sea floor. Red King Crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) are known to be very sensitive to changes in their environment. Temperature changes following the seasons are used to regulate breeding behaviours. Females must stay in warmer water than males to properly care for their eggs. Temperature and pH levels also regulate growth through moulting, therefore king crabs are particularly vulnerable to ocean acidification and climate change. In some parts of the world, squat lobsters have been recognised as a potential fisheries resource, however, well-established fisheries are currently found exclusively in Latin America.
Distribution
Worldwide.
Habitat
Mostly marine species, some species adapted to coastal or terrestrial life.
More Information
-
Animal Type
-
Fast Fact
Species of squat lobster have been known to live on the wreck of the Titanic.
-
Brief Id
A group of decapod crustaceans that resemble crabs, hermit crabs or small lobsters but unlike a true crab, have a very small fifth leg.
-
Maximum Size
1.8 m
-
Habitats
-
Diet
Omnivore
-
Diet Categories
Detritus, Crustaceans, Wood, Plants, Fruit, Insects, Fish
-
Endemicity
-
Commercial
No
-
Depths
Shore (0-1 m), Shallow (1-30 m), Deep ( > 30 m)
-
Water Column Locations
On or near seafloor
-
Taxon Name
-
Phylum
-
Subphylum
-
Superclass
-
Class
-
Subclass
-
Superorder
-
Order
-
Suborder
-
Infraorder