Summary
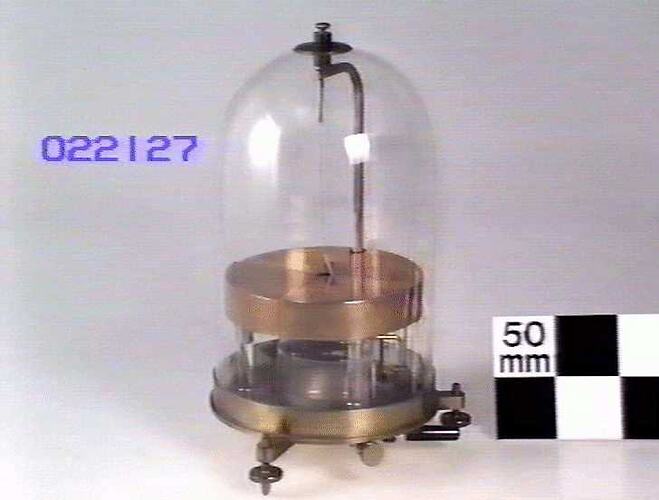
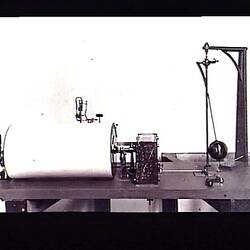
A simple Thomson type quadrant electrometer. Used at Melbourne Observatory.
An electrometer measures electrical charge.
The basic quadrant electrometer was developed by Lord Kelvin (Sir William Thomson) in the 1860s. The earliest versions were usually housed inside a "bird cage" or box. The bird cage electrometers got their name from the Faraday cage that was used to protect the instrument from stray electrostatic charges. In some cases, a glass bell jar protected them from the air currents which could affect their operation. The other common approach was to house the electometer inside a wooden box, the front of which was made of glass.
Physical Description
Instrument in wooden case.
More Information
-
Collection Names
-
Collecting Areas
-
Acquisition Information
Transfer from Melbourne Observatory, 1945
-
Inventor
Sir William Thomson (Lord Kelvin), England, Great Britain, circa 1860
-
User
Melbourne Observatory, South Yarra, Greater Melbourne, Victoria, Australia
-
Classification
-
Category
-
Discipline
-
Type of item
-
Overall Dimensions
25 cm (Length), 26 cm (Width), 40 cm (Height)
-
References
[Link 1] accessed 07/0/2010.
-
Keywords